Cloud Observability has new role-based access control (RBAC) features. Custom roles and log access controls can help you secure your log data and better align roles with users and teams.
What’s new?
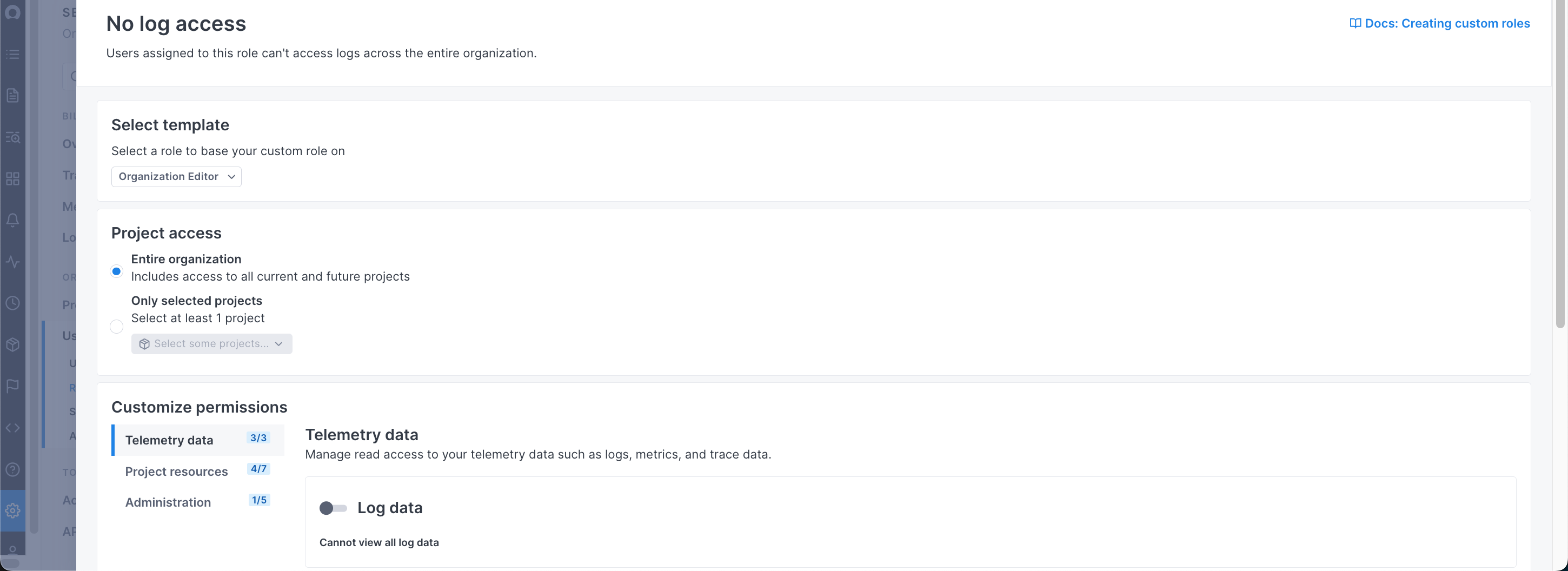
Custom roles
In addition to Cloud Observability’s standard roles, new custom roles let you configure access in ways that fit your workflows. For example, you can customize roles to manage:
- Log access for different users and teams.
- Project-specific edit access.
- Project-specific view access.
Custom roles give you more granular control, helping your teams and users work effectively and securely.
New permission structure
To help you navigate Cloud Observability permissions and create custom roles, we’ve restructured the permission categories. Here’s how they’ve changed:
- Old permission categories: Permissions were set at the organization, project, and feature levels.
- New permission categories: Permissions are now organized by:
- Telemetry data: Allow or restrict access to logs.
- Project resources: Manage project-specific resources like dashboards and alerts.
- Administration: Control account-level settings.
Log access control
A new Log data permission lets you manage access to log data. Before this release, Cloud Observability didn’t have a way to limit log access independently. Now, you can help protect sensitive data by defining who has access to logs.
Changes to standard roles
Previous Cloud Observability versions had seven standard roles: Organization Admin, Organization Billing Admin, Organization Editor, Organization Restricted Member, Organization Viewer, Project Editor, and Project Viewer.
With the custom roles release, Project Editor and Project Viewer are no longer standard roles. If anyone had a Project Editor or Project Viewer role, Cloud Observability auto-migrated those roles to custom roles. For example:
| Previous standard role | New custom role name |
|---|---|
| Project Editor in demo | Project editor in demo |
| Project Viewer in staging | Project viewer in staging |
There is an exception for Terraform users.
If you previously assigned Project Editor or Project Viewer with Terraform’s lightstep_saml_group_mappings or lightstep_user_role_binding resources,
users keep their access, and the roles still appear in Cloud Observability.
Next steps
To learn more about configuring custom roles and managing log access, see the updated documentation:
For more about user and role management in Cloud Observability, see User and role management and Plan your workflow.
Updated Dec 12, 2024
